
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
Blazor, released by Microsoft in 2018 as a free and open-source framework for web development, has evolved into a powerful tool. In this article, we take an in-depth look at Blazor, exploring its hosting models along with their benefits and limitations. We also provide insights into scenarios where Blazor development delivers the most value and demonstrate how EffectiveSoft professionals have successfully implemented this framework.
Blazor is part of the ASP.NET Core framework designed to build full-stack web apps with C#, .NET, HTML, and CSS. In Blazor web development, software engineers use a single programming language, C#, for both the backend and frontend instead of employing JavaScript and its frameworks like Angular on the client side. However, JavaScript can still be useful in some cases, and developers can easily call JavaScript code from C# code.
Razor components, also referred to as Blazor components, are fundamental building blocks used to create Blazor apps. They allow developers to build dynamic user interface (UI) elements, such as pages, buttons, or data entry forms using Razor syntax, C#, and HTML. These reusable components can be easily integrated to develop various web solutions, which significantly reduces development time and simplifies maintenance.
All Blazor apps can be deployed using three hosting models: Blazor Server, Blazor WebAssembly (WASM), and Blazor Hybrid. The Hybrid model extends development beyond the web to include mobile and desktop platforms. Below, we explore the key features of these Blazor hosting models.
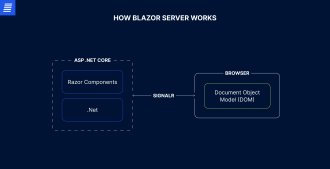
With Blazor Server, the web app runs on the server in ASP.NET Core, executing C# code in the .NET runtime. The server and client communicate through SignalR—a real-time messaging library—using the WebSocket protocol. SignalR pushes data between the backend and the frontend to manage events, UI updates, and even JavaScript function calls if necessary.
When a user interacts with the web app, the client side sends an event (user input) to the server through a constant SignalR WebSocket connection. The backend then processes the event and returns only the necessary changes to the client’s Document Object Model (DOM), updating the requested UI elements rather than all components on the page. This allows the web app to respond more quickly, delivering high performance and a streamlined user experience (UX).

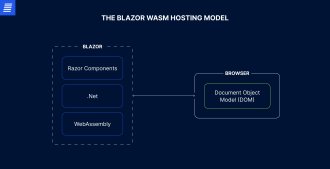
In the Blazor WASM hosting model, the web app runs entirely on the client side and uses WASM—a binary instruction format designed for browser engines—to execute C# code. When a user requests the app, the browser downloads it alongside a .NET runtime. The runtime leverages WASM to execute C# directly in the browser, enabling UI rendering on the client without a persistent connection to the server, except for the requested data fetching.

Blazor Hybrid combines web technologies with native .NET app frameworks like .NET Multi-platform App UI (MAUI), Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF), and Windows Forms to create cross-platform apps for the web, mobile, and desktop. In this hosting model, developers write a single codebase running on Windows, iOS, Android, and macOS and use BlazorWebView controls to render Razor components across these operating systems and various devices like tablets, mobile phones, and desktops. As it supports native functionality and UI elements through various .NET APIs, Blazor Hybrid is an ideal choice for developing web, mobile, and desktop apps that deliver native-like performance and flawless UX.


Leveraging Blazor is highly beneficial in the following use cases:

A one-stop service app designed for residents to facilitate digital engagement with property management companies, municipal services, and smart home devices and appliances.
EffectiveSoft’s developers successfully applied the Blazor framework to one of our client’s projects, creating a unified solution for the swift and precise processing of PCR tests.
The client, a Belgian point-of-care diagnostics company, tasked us with developing an algorithm-based diagnostic system that would integrate hardware, software, and reader firmware, while enabling seamless communication between them.
After developing a hardware testing solution for the client, our specialists moved to the next phase of the project, which involved building a Windows-based app to connect the hardware with the client’s proprietary algorithm along with a UI. Our team successfully completed this part of the project, delivering a WinUI desktop app that ran on the device’s hardware in kiosk mode.
However, over time, the client realized that remote access to the PCR system over the local network was necessary to maintain a sterile environment and decided to modernize the entire system. Given our productive collaboration in the past, the client turned to EffectiveSoft for assistance.
To revamp the system according to the client’s requirements, we switched to the Linux operating system instead of Windows and migrated from the WinUI desktop app to a web-based platform. EffectiveSoft’s specialists chose Blazor as the migration tool because it:
To deploy the web platform, our Blazor developers used the Blazor Server hosting model with its two rendering modes—static and interactive—which enabled the web app to deliver Razor components based on the required levels of interactivity.
By employing the Blazor framework, we helped the client easily migrate to the web-based solution, fostering remote accessibility to the PCR device, supporting relevant operations like reviewing test results, and maintaining the sterility of the system’s environment.
Blazor is a powerful and flexible framework that combines the advantages of web, C#, and .NET, empowering developers to create web, mobile, and desktop solutions that run seamlessly on a wide variety of devices. Has this tool made significant waves in the tech world? Absolutely. It has become not only a compelling competitor to JavaScript but also nearly a one-size-fits-all solution for full-stack and cross-platform development. Whether you’re seeking to build Blazor desktop apps or pursue Blazor cross-platform development, EffectiveSoft can help. Let’s connect now and discuss your project!

In addition to those mentioned in the article, the Blazor web development framework supports a wide range of features, including CSS isolation, virtualization, hot reload, and more.
Although Blazor is a viable alternative to JavaScript, it’s unlikely to replace JavaScript in the near future. This Microsoft framework supports various browser features, though not all of them, which may occasionally require the use of JavaScript snippets.
Blazor is definitely here to stay, with a promising future as Microsoft continues to evolve the framework by adding new features and expanding its full-stack and cross-platform capabilities.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659