
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
As e-commerce trends shift toward hyper-personalization, advanced technologies like machine learning (ML) become indispensable. Powered by ML algorithms, recommender systems analyze user preferences and predict what they are likely to buy in the future. Read on to learn how these systems work, why they are increasingly being adopted by e-commerce businesses, the challenges that accompany e-commerce recommendation software implementation, and more.
Like any other ML-based solution, recommender systems rely on data. The more data collected, the more accurate their predictions. This data can be gathered explicitly, through surveys of feedback forms, or implicitly, through user interaction with the platform. This data typically include:
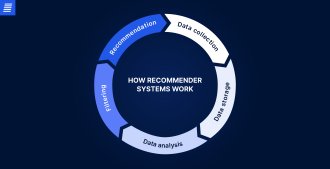

All the gathered data is stored in a database or data warehouse for further processing and analysis. Then, an e-commerce recommendation engine analyzes it to detect patterns and evaluate the matches between consumers and items. Based on this information, the system identifies the most relevant items to display and suggests products via a widget, email, or push notification. The user’s reaction to the suggested items is later used to fine-tune recommendations.
How recommendation systems work depends on their specific type.
Certain e-commerce platforms seem to be better at predicting user preferences than others. This is due to the diverse mechanisms functioning behind the scenes. Recommender systems use three main filtering types: content-based, collaborative, and hybrid.
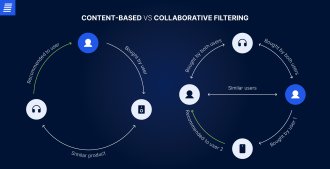

With content-based filtering, recommendations are based on product features. By analyzing them, the system suggests products similar to those a user has previously searched, viewed, or purchased.
If you have previously purchased a cream for sensitive skin, for example, the algorithms may recommend a face wash from the same brand or a similar cream from a different manufacturer.
Content-based filtering works well with limited user data but requires extensive descriptive data beforehand. This is time-consuming and challenging to implement with large product databases. In addition, content-based filtering doesn’t encourage users to discover new items.
Collaborative filtering is based on the assumption that similar users share similar tastes. Thus, e-commerce recommendation engines rely on the past preferences or behaviors of similar users to suggest products.
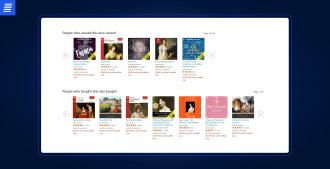

A perfect example of collaborative filtering is Amazon’s Customer who bought this item also bought section.
Unlike content-based filtering, collaborative filtering doesn’t require extensive product descriptions and can help users uncover new interests. Still, it presents several challenges:
To mitigate the weaknesses of the individual techniques, content-based and collaborative filtering are typically combined. These hybrid recommender systems offer the best of both worlds—leveraging behavioral data from multiple users along with descriptive product information.
Hybrid recommendation systems are ideal for making personalized recommendations even when there is little available data on the user. The only potential drawback of this approach is that it requires a more complex architecture and greater computing power, which typically only enterprise-level businesses can afford.
In brick-and-mortar stores, checkout counters are often stocked with small items that encourage impulse purchases, often complemented by a salesperson who can make effective recommendations or suggest additional items. In online stores, this function is performed by e-commerce recommendation engines, resulting in:
By suggesting complementary items, recommender systems encourage consumers to buy more products, thereby boosting total sales and AOV. In fact, 35% of all purchases on Amazon are driven by tailored recommendations generated by AI algorithms.
Relevant, appealing suggestions improve customer satisfaction and encourage shoppers to return. According to McKinsey, personalization can increase conversion rates by 10%–15%. Meanwhile, Salesforce reports that 37% of shoppers who clicked a recommended item during their first visit returned.
E-commerce recommendation engines gather valuable data about sales, customer behavior, trends, and more. This knowledge can be leveraged to adjust pricing strategies, improve recommendations, develop new products, predict product demand, and more.
Equipped with data on user behavior and preferences, recommender systems can improve ad targeting, ensuring that marketing budgets are allocated to audiences with high conversion potential. Customized messages tailored to specific consumer preferences can reduce customer acquisition costs by up to 50%, increase revenue by 5 to 15% and improve marketing ROI by 10 to 30%.
However, companies must address several challenges to achieve these benefits.

When implementing e-commerce recommender systems, it is crucial to anticipate potential complexities to ensure preparedness and efficient resolutions. Below are some of the most common issues e-commerce businesses encounter.
When a new consumer joins the platform or a new product is added, algorithms don’t have enough data to make meaningful recommendations. This is known as the cold start problem.
To tackle this issue, many recommender systems initially offer non-personalized recommendations, suggesting the most popular items either generally or based on the new user’s specific region, language, or age. For new products, a widget featuring new arrivals can be an effective solution until the system has analyzed enough search queries and user–item interactions to make personalized recommendations.
In online stores with thousands of products, users buy or rate only a few products. This leaves the system unaware of the user’s preferences for most other products, making it difficult for algorithms to predict other potential interests.
This issue is less common in hybrid recommendation systems, which leverage the strengths of various filtering techniques to enhance the recommendation process. Additionally, deep learning models can address the problem of sparse data by analyzing complex user–item relationships. These models can handle multivariate dependencies and predict interactions based on nonlinear patterns.
As an e-commerce platform expands, the system must process an increasing amount of data. This can hinder performance and reduce the system’s ability to make effective real-time recommendations unless highly efficient learning algorithms are in place.
Enhancing system scalability can be achieved through parallel processing, distributed computing, and well-designed data structures.
By focusing solely on what the user likes, recommender systems can create a “filter bubble,” preventing users from discovering things outside their usual preferences.
To avoid this, algorithms should offer variety by occasionally including less popular items in recommendations, encouraging customers to explore new options. The use of sophisticated techniques, like matrix factorization, can also help mitigate this issue.
When implementing a recommender engine into an e-commerce platform, decision-makers have several options to choose from.
These out-of-the-box engines enable companies to add personalized recommendations to their websites, apps, or platforms without needing to develop complex models from scratch. With preconfigured algorithms, these systems integrate with various services, platforms, and data formats to instantly deliver personalized recommendations with minimal customization. These features make plug-and-play recommender engines particularly attractive to companies without the resources to develop their own models.
The downside of plug-and-play systems is their limited customization and adaptability. While user-friendly and easy to implement, they may not meet specific business needs, resulting in less accurate and relevant recommendations compared to a tailored model.
These solutions offer ready-made recommender engines hosted on powerful cloud servers. They seamlessly integrate with websites and apps via APIs and can provide recommendations immediately after deployment thanks to pretrained models, eliminating the need for a lengthy training process.
Cloud-based recommender engines can be automatically updated and optimized, easily adapting to increased traffic and data while improving results based on new data.
However, using a third-party service limits the company’s flexibility and control over the algorithms, ties it to the vendor, and raises privacy concerns. Additionally, like plug-and-play recommender engines, pretrained cloud-based recommender services may not address specific business needs.
Although custom e-commerce recommendation software carries a higher initial cost, takes more time to build, and must be implemented and maintained by technical experts, it offers the most control and flexibility. This option may be right for you if:


If you decide to build a custom ML-based recommender system from scratch, the process will include the following stages:
Engineers gather relevant data from APIs, databases, or web scraping. They then preprocess the data by removing duplicates and filling missing values. As a result, the data is transformed into a format suitable for ML algorithms.
Analyzing data patterns and trends provides valuable insights, such as identifying the most popular products in a given season. This understanding of customer behavior is essential for informing model development.
This step involves creating the most relevant features or transforming existing ones to improve the model’s predictive accuracy and optimize training efficiency.
Depending on the business goals and data type, suitable ML algorithms with the appropriate filtering techniques are selected.
With the processed data and ML algorithms in place, it’s time to train the model to identify patterns and understand relationships between different variables.
To improve model performance and identify the optimal setup for personalized recommendations, hyperparameters—such as the number of layers, regularization parameters, and learning rate—are fine-tuned.
Once the model is trained, its effectiveness is evaluated using common metrics, including precision, recall, mean squared error, and A/B testing.
The developed, trained, and tested model is embedded into an existing app or platform, ensuring smooth operation in a real-world environment.
Integrating a recommendation engine, whether custom-built or off-the-shelf, is not a one-off process. Once implemented, it will require ongoing data collection, cleansing, and analysis, as well as bug fixing and algorithm optimization. This requires a professional IT team.
For businesses, e-commerce recommendation software offers clear advantages. By showcasing products and services that align with user interests, they drive increased sales and profits. However, implementing an effective recommender system requires a significant investment of resources, especially for those built from the ground up.
Although a custom-built recommender system may initially seem less advantageous due to upfront costs or setup time, it can ultimately yield the greatest profit. Its primary advantage is its ability to adapt to business needs rather than forcing the business to adjust to the system.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach. Whichever option you choose, we’re ready to dive deep into your business to provide the most suitable recommender system for your e-commerce solution.

Matrix factorization is a mathematical model that breaks down large datasets into smaller, more manageable entities to uncover the latent features or patterns behind user–item interactions.
In simple terms, it identifies users with similar preferences based on their past ratings and recognizes products that share qualities rated similarly by users. By analyzing this data, the system can predict ratings for products that have not yet been rated. For example, it may predict that a user would rate product A highly because other users with similar tastes rated it highly.
This allows the system to make relevant recommendations, even with limited user data.
Among the most popular languages for building recommender systems are Python, R, Java, Scala, JavaScript, and SQL.
The cost of recommendation software implementation depends on the complexity of the algorithm, data volume, and processing capabilities. Advanced deep learning methods and powerful processing capabilities require more resources. Additionally, the cost of e-commerce recommendation software implementation increases with more complex integration requirements and the need for high-performance infrastructure.
The best e-commerce recommendation software combines customizability, seamless API integrations, and a powerful analytics platform. Among the most popular off-the-shelf platforms are Algolia, Bloomreach, Clerk.io, Nosto, and Emarsys.
Sephora, Walmart, L’Oreal, and other global brands capitalize on the power of recommender systems. But the most successful example of an e-commerce recommender system is Amazon, the world’s largest marketplace. Amazon uses a sophisticated combination of collaborative and content-based filtering along with advanced techniques like deep learning, real-time data processing, and more. This hybrid approach enables highly relevant product suggestions, boosting sales and enhancing the customer experience. Up to 35% of Amazon’s total sales come from these recommendations.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659