Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

Medical biotechnology remains one of the most dynamic areas in the startup ecosystem. However, most potential therapies fail long before reaching FDA approval. The overall success rate in clinical drug development is only about 10%–15%, underscoring the difficulty of translating innovation into patient-ready products.
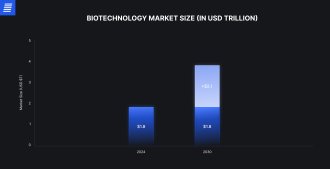

Source: Grand View Research
This article explores the primary scientific, regulatory, and financial hurdles biotech startups face, and practical strategies to overcome them.
Before entering human trials, biotech startups must demonstrate that their therapeutic concepts can translate from laboratory models into viable drug candidates. This preclinical phase often becomes a critical bottleneck. The core challenge is that success in petri dishes or mouse models often fail to translate to humans, with positive animal results proving poor predictors of human outcomes across most therapeutic areas.
Successful translation requires proving that the biological target drives disease, confirming therapeutic engagement at safe doses, and establishing acceptable safety margins. Yet even rigorous preclinical packages provide no guarantee of success. Smart startups mitigate this risk by prioritizing targets with strong human genetic validation, making early investments in predictive models like patient-derived tissues, and maintaining regulatory dialogue throughout preclinical development. Those that rush through preclinical development to preserve capital often face costlier failures in human trials.
The average duration of a clinical trial in the US is a surprisingly lengthy 6–7 years. The biotechnology sector’s regulatory complexity adds considerable time and cost, requiring extensive work to ensure that new patents and data submissions comply with regulations and avoid infringement issues.
During this lengthy process, external factors such as evolving science, shifting market demand, and updated regulatory requirements can change the viability of a therapeutic program. Even drugs that are initially promising may become redundant by the time they reach late-stage testing.
Typical clinical development timelines:
Overall, only about one in 10 drug candidates entering Phase I eventually reach the market.
The drug development process is best visualized as a funnel. Each stage narrows the field as complexity and cost increase.
The first phase of a clinical trial assesses safety and suitable dosing in healthy volunteers. Phase II evaluates efficacy and refines the dosing regimen in targeted patient populations. Phase III confirms clinical benefits and gathers evidence for regulatory approval.
The risk of inconclusive or negative data compounds at each level, which makes strong early-stage design essential to overall success.


Source: FDA
Recruiting an adequate number of treatment‑naïve patients is often one of the biggest challenges for startups. Additional constraints stem from factors like site capacity, competition for eligible participants, and feasibility.
Many biotechnology startups continue to use manual or outdated processes for managing clinical data and patient engagement, which are slow, error-prone, and expensive.
Automation, machine learning (ML), and specialized software tools can streamline patient identification, communication, and protocol analysis. Modern platforms can process and cross‑reference trial data thousands of times faster than traditional manual review.
EffectiveSoft’s biotechnology software development department designs custom tools to save start-ups valuable time and money. This can shorten the clinical trial process by months—or even years in some cases—and generate cost savings of hundreds of millions of dollars annually.

We built a web platform that helps stakeholders from the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and clinical research sectors engage with suitable partners to conduct clinical trials.
FDA approval marks a major milestone in the development journey, but it is not the finish line. Post‑marketing (Phase IV) studies are required to monitor long‑term safety, evaluate real‑world effectiveness, and detect rare adverse events. As these obligations add time and expense, they must be included in early financial planning. Once a new drug is released to the public, the FDA requires continuous safety monitoring and research over the course of the product’s life cycle. Phase IV studies involve patient data collection and new regulatory commitments, adding further costs that must be factored into the development process.
As startups shift from development-stage compliance to commercial-stage oversight, post-approval regulatory work introduces new activities. These include post-marketing surveillance, manufacturing and quality system compliance, life cycle management, and compliance with advertising, promotion, and distribution laws. To stay compliant and competitive, biotech startups should treat post-approval compliance as a strategic business function and invest in regulatory infrastructure.
Many biotech startups underestimate the total capital required to reach significant milestones. What’s more, relying on many smaller investors, each with too little “skin in the game,” is a poor strategy for startup biotech companies, as it makes it easier for those investors to walk away at the first major hurdle.
Pharmaceutical companies and venture capitalists, who provide much of the funding for biotechnology companies, often expect unrealistically fast launches and may pull the plug before the project has a chance to show meaningful results.
Most new biotech startups that end in failure simply run out of money before reaching significant milestones. Careful budgeting and modest savings can give biomedical startups a greater chance of long-term success.
However, many biotechnology companies rely on antiquated, time-consuming and expensive manual processes. Since each extra day of R&D can cost upwards of a million dollars, the company’s limited cash reserves can be depleted quickly—and often unnecessarily.
One issue most US biotech companies face is the fact that the industry is concentrated in a limited number of geographic locations.
While the clustering of biotech startups in the Bay Area, San Diego, and Boston can support collaboration and make it easier to recruit research staff, it also drives up competition and costs. Lab space, employees, and patients for clinical trials are expensive, further straining the resources of fledgling biotechnology companies.
In contrast, companies in Europe face less extreme cost pressures due to a more geographically distributed biotechnology sector.
High launch and marketing costs, along with uncertain reimbursement timelines, can cut resources and create cash-flow gaps after a long and resource-heavy R&D process. In addition to the costs of the commercial launch, there are additional expenses related to manufacturing scale-up, inventory and supply, and post-marketing studies.
Moving from lab to commercial manufacturing is not only resource-intensive, it’s technically demanding. Biotech startups must scale and optimize their processes to industrial production while maintaining product integrity. They must also navigate supply chain vulnerabilities, such as limited suppliers and the availability of raw materials.
Even with regulatory approval and manufacturing readiness, biotech startups may stumble on clinical adoption, which is earned through evidence, education, and trust-building. Physicians accustomed to familiar therapies may be reluctant to adopt new methods, viewing them as risky or insufficiently tested in real-world scenarios.
Understanding potential issues is crucial, but following best practices can help streamline the path to success.
Strong data infrastructure
Data quality and management play a significant role in R&D initiatives, as they rely on diverse information from multiple sources. A centralized data platform tailored to the specific workflows of a biotech company facilitates data analysis and regulatory compliance.
Technology and collaboration
The choice of a technology partner is key to a project’s success. An experienced software developer provides biotech startups with the digital resources necessary for management and advanced problem-solving. Leveraging automation and artificial intelligence (AI), companies can accelerate R&D, improve clinical trial design, and enable advanced analytics.
Risk management
Drug discovery and development are associated with numerous risks, including those related to compliance, finances, and operations. It’s crucial to have awareness of the competitive and regulatory landscape from the start, and be prepared to navigate them effectively. This requires a strategy for addressing potential concerns, along with proactive risk planning and mitigation measures.
Scalable architecture
Biotech systems should evolve as research expands, supporting long-term goals. Scalable data storage, modular components, and containerized architecture simplify the management of growing data volumes and system updates, maintaining consistency without compromising productivity and speed.
Continuous compliance
Biotechnology is a highly regulated area, with FDA, EMA, GxP, and other standards ensuring the high quality and safety of innovations. Building a regulatory-ready process from the outset helps biotech startups establish credibility, gain public trust, and reduce the risk of fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage. Moreover, retroactively fixing data and documentation issues or filling process gaps requires significant resources.
Medical biotechnology offers innovators and investors the potential for market-beating returns, but it comes with an extremely high risk of failure. Each new drug program faces steep odds against success.
While the risk of a clinical trial failing to deliver the desired results is inherently difficult to avoid, many of the project costs biotech startups face are relatively easy to control and optimize. For example, leveraging medical biotechnology software and choosing the right development partner can significantly reduce costs by streamlining processes, automating tasks, and maintaining compliance. Reach out to us to learn how we can help and launch your project.

A biotech startup leverages biological processes and innovations to develop new products or technologies. This can include drug development, genetic engineering, medical diagnostics, biological research, biomanufacturing, and therapeutics. The aim is to address challenges in healthcare, agriculture, or the environment by applying cutting-edge biological science and technology.
Biotech startups face risks including regulatory hurdles, lengthy and costly R&D processes, and uncertainties in obtaining patents. Market adoption can be slow, and competition is fierce. Ethical concerns and public perception may affect investor and consumer trust. Technical challenges, such as reproducibility issues and data integrity, can also pose significant risks to the success of biotech startups.
Custom software development can support biotech startups at every stage, from data collection and analysis to clinical trial management. These solutions enable healthcare biotech companies, partner organizations, and healthcare providers to collaborate effectively, ensure compliance, streamline processes, and improve decision-making. AI integration can also accelerate discovery. Reach out to our experts to learn how custom software can assist your workflows.
Since biotech companies handle vast quantities of experimental, clinical, and regulatory data, they require a management system to handle it efficiently. A robust data management system helps maintain accuracy and traceability while enabling compliance with FDA and EMA standards.
Various tools and platforms are used in healthcare biotech R&D. Some of the most popular are laboratory information management systems (LIMS), scientific data management systems (SDMS), electronic laboratory notebooks (ELNs), and project management platforms tailored to healthcare R&D teams.
By using effective digital tools, biotech companies can automate documentation, version control, audit trail, and more, ensuring compliance with FDA, EMA, GxP, and other standards.
A technology partner designs secure, scalable, and compliant digital solutions tailored to the needs and requirements of healthcare biotech companies and their unique R&D workflows. This helps biotech startups focus on innovation while a software development company deals with operational bottlenecks.
AI and ML play a key role in transforming healthcare biotechnology and drug discovery, making them faster, more efficient and precise. AI/ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify hidden relationships and correlations, make predictions, perform virtual screenings, and more.
Investing in digital infrastructure early is a good strategy for biotech startups. Building a solid foundation from the outset supports data hygiene, infrastructure scalability, security, compliance, integration, and analytics. Without it, biotech companies risk data chaos, tech debt, regulatory issues, and operational bottlenecks.
Yes, software can significantly reduce the cost of drug development by enabling AI-powered data analysis, automating repetitive and time-consuming processes like data collection, and enhancing decision-making at every stage of R&D. Moreover, digital tools accelerate research, shorten development timelines, and increase success rates through smarter, data-driven operations.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659