
Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.

In this article, we will find out what IoT in smart manufacturing is and what benefits and challenges it brings to the industrial field.
IoT refers to a network of physical objects that interact with each other via the Internet, often with minimal human intervention. IoT encompasses devices with embedded sensors and software for collecting and exchanging data with people and/or other connected devices. In many cases, IoT is associated with the “smart” prefix: smart home, smart watches, smart city, etc.
Let’s explore how IoT works. First, we should point out that IoT includes several basic components: devices, connecting networks, IoT platforms (or IoT hubs), and also end users or systems.
Simply put, the process is the following:
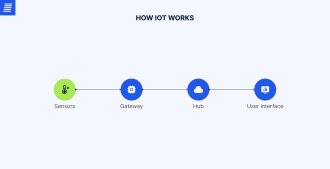

An IoT platform is a centralized software solution for connecting, managing, and analyzing data from end devices and applications. This platform acts as a sort of place where IoT components can interact with each other.
Modern IoT platforms enable:
There are many off-the-shelf platforms on the market, but some of the most robust IoT solutions for manufacturing, according to Gartner, are Cumulocity Platform, AWS IoT by Amazon, Microsoft Azure IoT, ThingWorx by PTC, and Oracle IoT Cloud.
In recent years, IoT has found widespread use in the industry as a way to solve a multitude of tasks. IoT used for industrial purposes is commonly referred to as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). IIoT systems are being increasingly adopted by many manufacturers. About 46% of manufacturers already collect and use data from smart sensors to improve production processes while about 85% of manufacturers believe smart manufacturing is the main driver of competitiveness. Studies predict that the IoT in the manufacturing market will grow at a rate of 25.33% CAGR from 2025 to 2030.
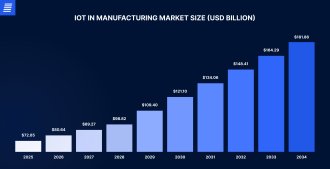

Source: precedenceresearch
IoT can be implemented in many production processes that are automatable, especially when there is a need for remote monitoring of the state of objects and data collection for future analysis. However, it’s no use introducing technology just to introduce it. There must be value. To figure out what the value is and how IoT can help your enterprise, it is necessary to delve into the specifics of your business. Here are some of the most common cases.
With IoT, manufacturers can get an overview of manufacturing processes and the state of the product at all stages, from the delivery of raw materials to the shipment of the final product.
Computer vision systems and sensors keep an eye on whether production equipment is operated in accordance with standards: thermometers monitor the temperature to avoid overheating, vibration sensors ensure that the amount and frequency of vibration in the equipment is within normal limits, and so on. The systems can also send signals to the control panel to notify personnel if machinery is malfunctioning.
Smart devices collect data from equipment and transmit it to the cloud or local servers for detailed analysis, providing information on machine usage parameters: setup times, downtime, minor shutdowns, and more. Therefore, the staff can keep track of performance parameters and predict potential problems.
The process control helps promptly discover a defect in a machine and make a decision to switch to a back-up system. This approach helps prevent full equipment breakdowns, reducing repair costs and avoiding production halts.
The safety of employees and systems is one of the main priorities of any industrial organization, so it is imperative to create the most secure environment possible. That is why companies take measures to restrict unauthorized access to strategically important production objects and to limit access of people to hazardous areas. To ensure security of the enterprise territory, personnel and assets, it is essential to consider all entry points and potential threats. In order to solve this issue, new technologies are being introduced.
Although digital locks, RFID card readers, and security cameras have been around for years, the IoT technology has taken access control and data-driven security to a new level. The fusion of IoT devices with low power consumption, the cloud, and advanced security technology has led to the creation of sophisticated, comprehensive, and fault-tolerant access control systems.
A sophisticated access control system includes a variety of devices (sensors, smart electric locks, biometric readers, and smart security cameras) that help monitor the presence and movement of people throughout the area. With these IoT-enabled devices, it is possible to monitor the entire security system and remotely track who and when enters the territory.
Smart wearable devices integrated in the factory help keep track of workers’ compliance with the safety regulations. No matter how responsible and disciplined employees are, they are still people who might break rules, intentionally or not. For instance, they may forget to wear a helmet or a respirator. Smart systems practically exclude such a scenario. Smart cameras and smart bands that read movements assist in controlling whether a worker in the shop is in full gear. Special medical examination systems, in turn, reduce the chances of a person with a fever, high/low blood pressure, or intoxication being at work.
IoT in manufacturing has enormous potential in the green economy. The technology can facilitate sustainable initiatives such as environmental monitoring and energy optimization. Smart sensors can detect excess heat, air pollution, radiation, or noise and send alerts, so that the staff can get the situation under control. Moreover, some IoT-enabled devices are programmed to automatically normalize the parameters.
Automatic energy control through a smart grid can improve utility operation and performance. So, the resources are distributed more accurately, and the real needs are addressed without energy waste. Furthermore, in case of emergency IoT devices can level usage between critical and non-critical infrastructure.
Many tasks can be done with sensors, saving thousands of man-hours. Meanwhile, the staff can work on more urgent issues. This way, you can redistribute personnel more efficiently, reducing the production costs.
To sum up, IoT in manufacturing allows businesses to:
All this can save you millions or even billions of dollars. Yes, transforming your enterprise could be expensive. The initial cost of the digital optimization may become one of the most challenging factors, but imagine how much you’ll save in the future.
Practically, every business is based on three pillars: quality, cost, and time of production or service delivery. If businesses want to retain and increase their financial performance, they need to make a product uniquely, efficiently, and quickly.
Implementing IoT can be of great help in this regard, but such a solution initially requires a reasonable investment, and then you have to wait for a while until the money pays off. But what to do if you don’t have funds right now and you understand that IoT is the best choice for your business? The traditional option is to look for an investor. But there is another one that is gaining momentum—Product as a Service.
Product as a Service is a business model when the product is provided for use via a lease agreement. IoT-enabled Product as a Service transforms the way manufacturers sell goods and services and the way companies consume them.
At first glance, this model may seem a perfect option as it reduces the risk of asset investment and performance risk. The cost of the technologies required to implement the IoT-enabled Product as a Service business model is going down thus making them more affordable. The use of open-source technologies and access to out-of-the-box solutions to integrate into IT and OT systems considerably reduces development and implementation costs.
In addition, this model eliminates the need for staff to maintain and support assets since IoT-enabled Product as a Service vendors take over product support and maintenance in exchange for regular payments. This encourages manufacturers to produce more robust, long-lasting, and easy-to-use IoT products.
However, there is the flip side of the coin. This model is more efficient in the short term, but usually more expensive strategically, while custom implementation on top of an out-of-the-box platform is more efficient in the long term, but requires more investments from the start.
The amount of data generated in the IoT ecosystem is constantly growing. However, not all information is relevant to an enterprise. Therefore, corporate data centers are gradually moving toward operational data processing in which edge-IoT computing can help. As the name implies, it combines IoT and edge computing technologies.
Edge computing brings data processing as close as possible to the IoT device, which in turn analyzes the data and delivers instant results. So, the data is analyzed right at the collection point. Thus, this process eliminates latency and conserves bandwidth.
IoT and edge computing are powerful technologies that can save businesses a lot of time and effort. Using IoT and edge computing together can be a great way to achieve different goals within the same infrastructure by rapid data analysis in real time.

5G technologies are real game-changers and offer enormous potential for IoT. A huge quantity of connected devices (the number grew to 18.8 billion in 2024) and a large volume of consumed data require faster technologies such as 5G.
The technology lessens the need for physical networks: everything is wireless. With 5G, the data transfer rate increases dramatically. In addition, the high bandwidth of the new network reduces latency and response time. So, 5G enables data transmission in real time, as the seamless exchange of data between machines, systems, robots, and people is an integral part of industrial production.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and IoT usually complement each other. In this case, we are referring to the Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT), i.e. networks of IoT-enabled devices controlled by AI.
While IoT systems can only collect and organize data, AIoT systems can go further. AI plays the role of the “brain” inside IoT devices. It is due to AI that it is possible to process, analyze, and make informed decisions.
Furthermore, AI performs long-term analysis and builds algorithms enabling enterprises to conduct predictive analysis based on multiple possible scenarios. Therefore, businesses can promptly assess and respond to risks and make changes to operational parameters.

Although IoT systems carry significant business value, it is worth mentioning that there are still some issues to be solved by developers.
The widespread adoption of Internet-connected devices has increased the potential entry points for cybercriminals. As a result, cybersecurity in the workplace has become an increasingly urgent concern. Organizations pursuing digital transformation and IoT implementation must adopt a more robust and adaptive cybersecurity strategy. A cyberattack can result in unauthorized external control of systems, leading to potentially malicious and destructive outcomes.
Protecting your data and safeguarding your IoT system from breaches is a necessity. A strong security framework should include proactive measures, such as access controls, security audits, backups, and incident response plans. Frequent system updates help reduce security vulnerabilities and maintain compliance with the changing regulatory requirements.
Another important challenge is integrating all IoT devices into a company’s infrastructure, especially given the variety of communication protocols. This becomes even more complicated when operating within an ecosystem of vendors, logistics companies, or other partners, where compatibility is essential.
To get around this problem, decision-makers should engage with all stakeholders and stay informed about evolving IoT standards. In addition, choosing widely adopted IoT communication protocols can help, as they typically offer stronger security features and are more likely to be compatible with your partners’ systems.
Legacy systems still used in manufacturing can hinder the adoption of new technologies. They pose serious technical and business challenges, including compatibility issues, security risks, high implementation costs, and infrastructure limitations.
In addressing these issues, manufacturers use a range of helpful strategies. First, it’s critical to assess and map the existing legacy infrastructure to identify integration points and understand limitations. To bridge the gap between old and new systems, organizations can deploy IoT gateways, which enable legacy systems to transmit data without major modification. A layered architecture helps ensure scalability and flexibility. Throughout the integration process, manufacturing companies should adhere to data security best practices.
The adoption of IoT in manufacturing offers significant advantages, including improved control over the process and more efficient resource allocation. However, implementing IoT also presents several challenges. To fully capitalize on the technology and achieve operational excellence, it’s important to meet the right partner on the path.
At EffectiveSoft, we have dedicated professionals in IoT software development. Our experts will help you determine what IoT software solution is uniquely suited for your business, and our developers will implement this idea. All you need to do is to send us a request.

The Internet of Things (IoT), or Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), refers to the use of connected devices, sensors, and machines that collect and exchange data to improve efficiency and productivity and achieve automation in manufacturing processes.
In manufacturing, IoT is used for real-time monitoring and process control, predictive maintenance, managing accesses and environmental conditions, ensuring personnel safety, detecting defects and controlling quality, tracking assets, and more.
Often, manufacturers use sensors for temperature, vibration, humidity, etc., smart meters and energy monitors, RFID tags and scanners, and edge devices and gateways.
Some of the key IoT benefits for manufacturers include improved operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, reduced downtimes through predictive maintenance, better inventory and logistics management, data-driven decision-making, and cost savings over time.
By integrating IIoT with AI, machine learning, and other advanced analytics, manufacturers can unlock practical insights and predictive capabilities that enhance decision-making and operational efficiency. Acting as the brain in the IIoT ecosystem, data analytics turns a network of connected devices into a smart, self-optimizing industrial system.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659