Contact us
Our team would love to hear from you.
Smart transport supported by IoT is growing at a staggering rate. About 75% of new cars sold in 2024 included embedded cellular connectivity, and it’s estimated that over 90% of vehicles sold in 2030 will be connected. The automotive industry is integrating the latest trends in telecommunications, computer technologies, programming, and machine learning to produce safer and more comfortable vehicles. Automobile manufacturers also understand IoT’s potential and seek to capitalize on its benefits. Let’s look at how IoT is used in the automotive industry and what possibilities it creates.
IoT refers to interconnected devices that collect, exchange, and act on data via the Internet with minimal or no direct human intervention. Automotive IoT involves integrating these technologies into vehicles and related systems to create smart, efficient functionality. While futuristic ideas like fully self-driving and flying vehicles attract attention, the most significant transformation today is driven by connected systems, sensors, and automation.
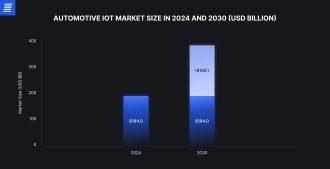

Source: Grand View Research
Solutions and technologies to connect vehicles are already transforming modern vehicles. The following are some of the most common use cases.
Automotive IoT has transformed fleet management. Sensors such as GPS and OBD2 devices embedded in different vehicle components collect data on speed, location, idle time, fuel consumption, load, temperature, driver behavior, and more. This data is then transmitted wirelessly to the gateway and fleet management platform for analysis.
IoT solutions support fleet management operators in a variety of ways. With IoT, they can:
As a result, fleet management has become smarter, saving time by eliminating much of the manual work required by traditional approaches.
Always-green traffic lights, available parking, reduced accident risk, and safer mobility for people with disabilities may sound utopian, but IoT-enabled vehicles are already transforming these possibilities into reality.
Internet-enabled intelligent systems allow modern vehicles to communicate with each other as well as the outside world. In this sense, vehicles are connected to everything. Depending on the “interlocutor,” we can distinguish between the following patterns.
Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V)
Cars connect to each other and share relevant information (location, engine temperature, route, speed, etc.) in real time. If dangerous conditions occur in a vehicle, the drivers of nearby cars receive a warning so they can take measures to prevent an accident.
Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I)
Cars connect to the surrounding smart traffic infrastructure (toll booths, parking, etc.) and receive data about traffic light signals, parking space availability, and so on. For example, by connecting to traffic lights, smart cars can inform their drivers about the amount of time until the next green light.
Vehicle-to-pedestrian (V2P)
Cars connect with vulnerable road users (pedestrians, cyclists, public transport passengers, etc.) and receive information about their proximity. Pedestrians are notified of approaching vehicles, including their speed and direction, allowing them to detect and predict the trajectory of vehicles at a particular time.
Vehicle-to-device (V2D)
Cars and drivers interact via a mobile app. Drivers can use their smartphones to open and close the car, start and stop the engine, check the gas or the battery level, park the car from outside, and more.
Vehicle-to-network (V2N)
Cars connect to mobile networks to exchange data with the cloud in real time.
IoT solutions can be used to track vehicle parameters and notify the driver of potential automotive system failures. All modern automobiles are equipped with wireless connections and sensors (including position and speed, air flow, exhaust emission control, temperature, pressure, and more). The system gathers the relevant data from the sensors, compares it with the preset limits for the vehicle type, and alerts the driver to any discrepancies.
Connecting cars to the cloud enables the real-time synchronization of this data. In addition, car owners can use smartphones to view information about their vehicles and receive notifications through their online accounts.
This ability to identify and prevent breakdowns before they occur saves time, money, and anxiety while improving overall road safety.
Modern in-vehicle infotainment is no longer an outdated push-button radio receiver but a whole system that connects to all smart car technologies, including ADAS, V2X connection solutions, sensors, and more. Some manufacturers develop their own software, while others integrate off-the-shelf Apple and Google products like CarPlay or Android Auto. These products aid in navigation, play audio, enable hands-free calls, provide access to third-party apps like Spotify, and more.
There is one area where IoT in the automobile industry has already turned fiction into reality: autonomous vehicles, which represent one of today’s main automotive IoT trends.
Many people imagine self-driving cars as providing complete autonomy and a virtual robot driver they can talk to, but the reality is quite different. Autonomous cars are already widely used, but they are not yet fully robotic cars that can move without human intervention.
According to a classification system by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), there are six levels of driving automation:
Level 0 (no automation): The driver must control everything.
Level 1 (hands-on): The automated system acts as a driver’s assistant. Cars have adaptive cruise control, parking assist systems, and lane departure warning systems.
Level 2 (hands-off): Cars are partially automated. Vehicles independently control the gas and brake, but the driver must always monitor the situation to immediately switch to manual control if necessary.
Level 3 (eyes-off): This level is characterized as conditional automation. The car can drive on its own, but the autopilot is effective only in ideal road conditions. The driver should be ready to intervene at any time, for example, if there is a risk of an accident.
Level 4 (mind-off): The level is defined as high driving automation. The car can do everything Level 3 cars do, but can also solve complex traffic situations. However, unmanned capabilities are not limitless yet. Examples of this level include Cruise and Google’s driverless taxis, which can only drive on the roads they have been trained on.
Level 5 (no driver): This is full driving automation. The car drives with no human intervention.
Level 0–2 cars are most common, while cars at Levels 3–4 are currently undergoing tests and gradually entering the market (e.g., Mercedes-Benz Level 3 approval in Germany and the U.S.). Level 5 vehicles are still under development and do not transport passengers yet.
Studies suggest that autonomous cars will make the roads safer. Because most accidents are caused by human factors such as alcohol intoxication, fatigue, and stress, it makes sense to eliminate these risks. That’s where robotic cars can help.
To move without drivers’ assistance, autonomous cars must be equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) to process the information from the sensors and cameras and command the car. They must also be equipped with GPS, an inertial navigation system (INS), and many other devices, including:


Developing software for the automotive industry is a challenging and lengthy process. Before embarking on this journey, it’s critical to understand the current trends and assess the potential risks.
It is essential to analyze off-the-shelf solutions and evaluate all their pros and cons. While these tools can work for some use cases, custom-built solutions are often better suited for specific project needs, especially when integrating with existing vehicle systems and hardware. Choosing the right path depends on performance needs, integration requirements, regulatory context, and system architecture.
Once you’ve conducted the necessary technological and market research, the next step is to define your app concept: how it will work, the specific purpose it will serve, and who it’s designed for (drivers, businesses, passengers, etc.). Each of these elements should be considered carefully while keeping the company’s resources in mind.
Business analysts or domain experts can help streamline this process by assessing requirements, evaluating risks, and clarifying system expectations. This early analysis ensures that development is aligned with business goals and technical constraints. Entrusting the project to a specialist saves time and effort while ensuring you receive a cutting-edge app.
Once the preliminary research is complete and a blueprint is in place, the development team gets to work.
Many developers can build an ordinary app for a car, but only the most skilled can develop an app that works well with the built-in systems, ensures hardware and software connectivity, and enables connections to third-party APIs.
Automotive IoT projects require experienced engineers who understand in-vehicle systems, cloud platforms, and communication protocols. The team should be able to integrate software with embedded hardware, ensure secure data transmission, and support interoperability with third-party APIs.

We developed and integrated a voice assistant powered by generative AI (GenAI) agents connected to the client’s automotive infotainment system, streamlining interactions for Tesla drivers and increasing safety.
The automotive industry offers a wide range of IoT solutions. Choosing the right tech stack depends on the specific requirements of the system, such as latency, connectivity, security, and the target vehicle platform. Experienced developers evaluate each option on a case-by-case basis.
To avoid distracting drivers, car app interfaces should be simple and intuitive. Hiring experienced UX designers ensures your solution meets these requirements while delivering an enjoyable experience for drivers.
Security is one of the biggest challenges of implementing IoT technologies in the automotive industry. Modern cars are not isolated machines but components of an interconnected ecosystem that includes smartphones, autonomous driving infrastructure, cloud services, and more. If systems are poorly protected, cars can become dangerous weapons in the hands of cybercriminals, exposing users to data breaches, loss of system control, and even life-threatening situations.
When designing a security system, engineers should approach the issue from the perspective of how it will respond when, rather than if, an attack occurs. Protecting all vulnerabilities requires mapping every potential path a cybercriminal might take.
To ensure network and app security, several basic precautions must be followed:
However, these steps are just a small part of what it takes to launch a secure app. Security measures alone are not enough; comprehensive testing of automotive IoT systems is essential to ensure safety and reliability before deployment.
While many companies have only just started talking about IoT-enabled vehicles, others have already made history. Here are some real-world cases:
In 2022, Mercedes-Benz introduced DRIVE PILOT, a conditionally automated driving system (SAE Level 3) that operates under certain real-life conditions, which vary depending on the region. Once activated, the system begins to regulate speed and distance, ensuring the vehicle stays in its lane. It relies on the environmental sensor system of Mercedes-Benz’s Driving Assistance Package, along with cameras and other sensors such as LiDAR (light detection and ranging), to ensure safety and precise positioning. DRIVE PILOT is already available in Germany, China, and some U.S. states. The company continues to enhance the system using AI to achieve fully automated driving.
Founded in 1996, OnStar is a subsidiary of General Motors (GM). It evolved from GM’s Project Beacon, which aimed to bring wireless communications to automobiles. Today, OnStar focuses on driver safety and security, offering telematics-based insurance services. Using telematics control units (TCU), cellular and GPS antennas, and a range of integrated vehicle sensors, OnStar delivers automatic crash response and emergency assistance, remote diagnostics and vehicle health monitoring, remote commands and access, stolen vehicle recovery, and navigation and route guidance.
Toyota Connected was launched in 2016 as a dedicated connected mobility hub for Toyota globally. By embedding connectivity modules (cellular, cloud, data analytics) into vehicles and providing apps and cloud services, Toyota Connected turns cars into network devices. The system collects data from the vehicle, transmits it via cellular communication to cloud back-ends, analyzes and stores it, and provides services to users via apps. Key services include safety and emergency, remote vehicle control and convenience features, navigation, assistance, driving support, and fleet management for businesses.
IoT software is rapidly becoming an integral part of modern mobility. Its value is clear: smarter maintenance, greater visibility into transportation processes, increased road safety, and a more engaging in-vehicle experience. Together, these innovations are reshaping how vehicles operate and how users interact with them.
If you’re ready to turn automotive IoT into a competitive advantage, EffectiveSoft is here to help. Our experts cut through complexity, build solutions that scale, and deliver on their promises.

Automotive IoT refers to the integration of Internet-connected sensors, devices, software, and cloud systems into vehicles and the broader transportation system. This connectivity enables cars to collect, exchange, and analyze data in real time, helping improve safety, efficiency, and UX.
IoT systems improve safety and compliance through continuous monitoring of the vehicles, the environment, and the driver, using real-time data to prevent accidents, correct unsafe behavior, and ensure vehicles meet legal requirements. IoT-enabled automated documentation and accurate operational data management also help ensure compliance.
While connectivity offers significant benefits, it can also introduce cybersecurity risks, as more connections mean more potential entry points for attackers. Weak or outdated software, insecure wireless communications, and keyless entry systems all increase system vulnerability. However, these risks can be mitigated with a multilayered, end-to-end security strategy. An experienced IoT partner knows how to address security challenges across hardware, software, communication, and cloud. Contact EffectiveSoft’s experts to learn more about our security measures.
OTA updates allow manufacturers to remotely update software in vehicles through cellular or Wi-Fi networks, just like with smartphones. These updates are critical, as they improve functionality, fix vulnerabilities, and keep vehicles safe and compliant without the involvement of the manufacturer or a dealership.
IoT-enabled systems collect real-time data from vehicles, infrastructure, and the environment, which is then used for descriptive, predictive, diagnostic, and other types of analytics to improve safety, efficiency, and user satisfaction. This can include predictive maintenance, route optimization, fuel efficiency analytics, driver scoring, and anomaly detection.
The development timeline varies depending on the complexity, regulations, integration requirements, and other factors—from 6-12 months for a simple system to over a year for a more intricate solution. Reach out for a project estimate tailored to your specific needs.
The cost of implementing an automotive IoT system depends on numerous factors, including hardware, connectivity, cloud services, integrations, and ongoing support. Contact our team to learn more and get a custom project estimate.
Can’t find the answer you are looking for?
Contact us and we will get in touch with you shortly.
Our team would love to hear from you.
Fill out the form, and we’ve got you covered.
What happens next?
San Diego, California
4445 Eastgate Mall, Suite 200
92121, 1-800-288-9659
San Francisco, California
50 California St #1500
94111, 1-800-288-9659
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
One Oxford Centre, 500 Grant St Suite 2900
15219, 1-800-288-9659
Durham, North Carolina
RTP Meridian, 2530 Meridian Pkwy Suite 300
27713, 1-800-288-9659
San Jose, Costa Rica
C. 118B, Trejos Montealegre
10203, 1-800-288-9659